Publications
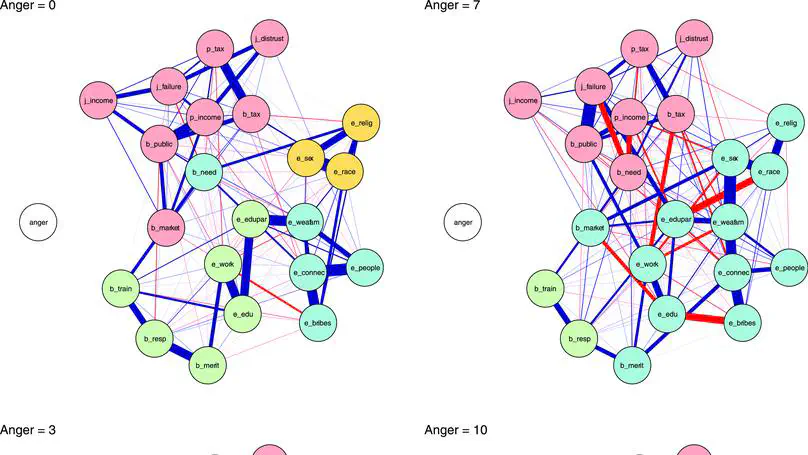
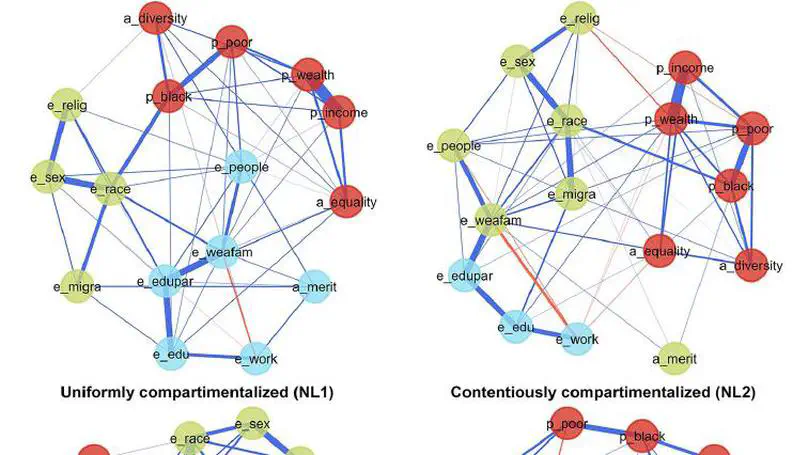
This study examines inequality belief systems in the U.S. using data from the 2019 ISSP Social Inequality module, showing they form cohesive small-world networks centered on perceptions of inequality and support for redistribution. By applying network models and simulations, it demonstrates that anger strengthens and polarizes these systems, while changes in central attitudes trigger broader shifts across beliefs.
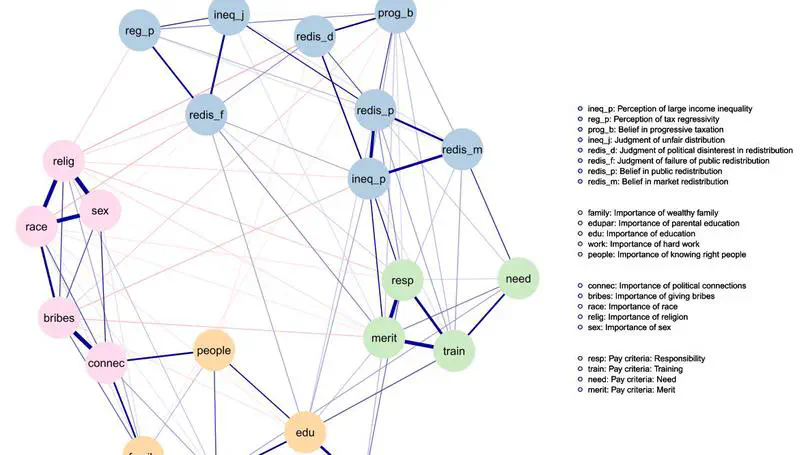
This article constitutes the first application of the attitude network approach to peoples’ views on inequality. We adopt a network model in which nodes represent survey variables and edges their conditional associations. This allows us to conceptualize perceptions, beliefs, and judgments about inequality as a network of connected evaluative reactions.
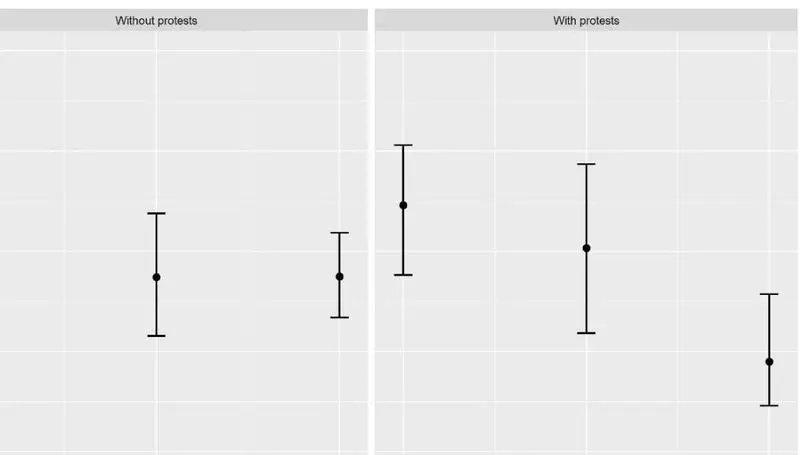
This article addresses this issue through a quantitative analysis of the projects submitted for EIA in Chile between 2009 and 2019, unpacking how the presence of social protest affects the qualification granted by public services and the time elapsed between when the project is presented and finally receives qualification.
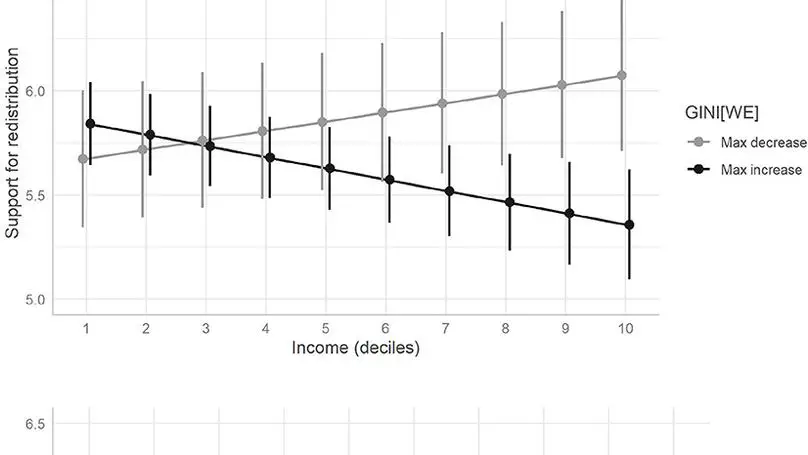
A series of theories focused on self-interest have continuously established a negative link between people’s income and their support for the reduction of inequalities through redistribution. Despite this, the evidence is scarce and sometimes contradictory while its study in Latin America is almost non-existent. Using data from the LAPOP Survey between 2008 and 2018, a longitudinal dimension is considered for the first time in the measurement of Latin American redistributive preferences, using hybrid multilevel regression models.
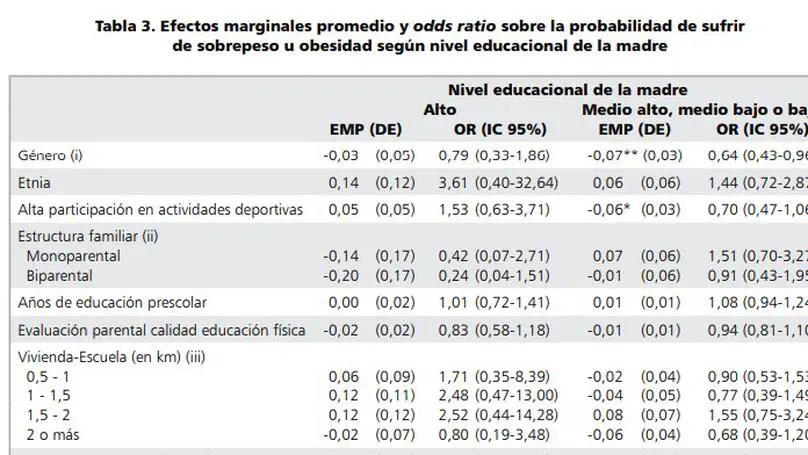
This article aims to identify individual, social and environmental factors that affect the likelihood of adolescents to become overweight or obese. We used physical condition data of a sample of 900 urban eighth grade students from Santiago, obtained in the 2011 National Study of Physical Education. This information was complemented with georeferenced data from the place of residence of students and the environment in which they live.